Get unique, complex parts easily. No matter your requirements, Chaoyi Spring creates hard-to-produce coil springs and wire forms.
Let us help you create the custom wire form you need, from S-hooks and J-hooks to utility hooks and more.
We work closely with customers across a wide range of industries, helping them design and manufacture made-to-order parts.
Why choose Chaoyi Spring? We prioritize customer-focused collaboration, modern equipment and the latest technology to make your parts per print.
Find the information and guidance you need, from measuring a spring to learning about materials, placing an order and much more.
In the world of mechanics and engineering, springs and torsion elements are fundamental components, each playing crucial roles in a wide range of applications. While seemingly similar at first glance,


In the world of mechanics and engineering, springs and torsion elements are fundamental components, each playing crucial roles in a wide range of applications. While seemingly similar at first glance, torsion and spring mechanisms differ in their design, function, and applications. This article delves into the core distinctions between torsion and spring, providing a comprehensive understanding of their unique characteristics and applications. We'll explore how each mechanism works, examine their strengths and limitations, and illustrate their use in everyday objects and complex engineering systems.
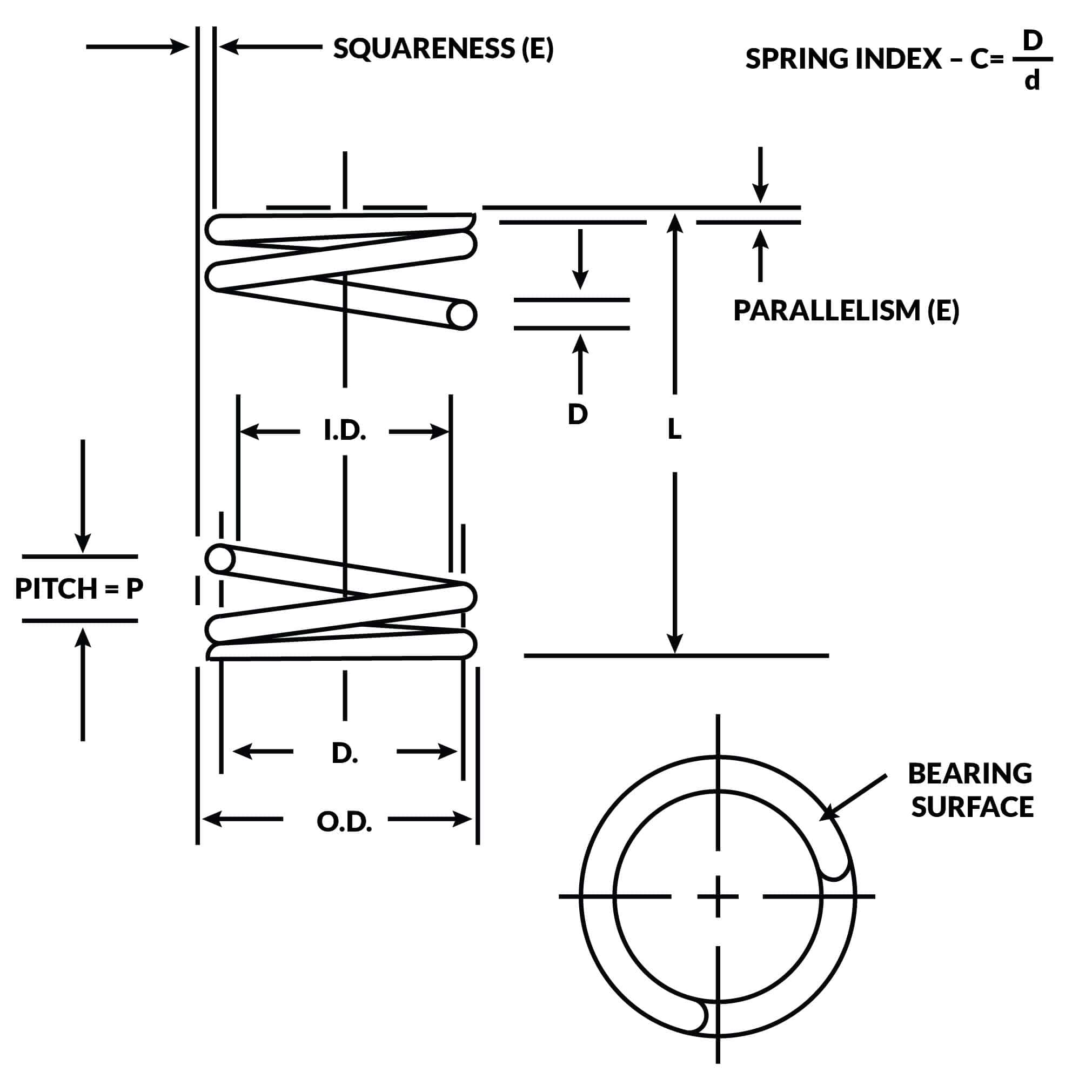
Torsion refers to the twisting or rotational force applied to an object. Imagine holding a rod at both ends and applying a force that makes it twist. This twisting action is torsion, and the object experiencing this force is said to be in torsion. The twisting force, measured in units of torque (Newton-meters or foot-pounds), results in a twisting deformation within the object.
Torsion springs, often referred to as twist springs, are designed to resist twisting forces. They are typically made of coiled wire that, when subjected to a twisting force, exerts a restoring torque proportional to the angle of twist. Imagine a door hinge. When you open the door, the hinge twists, and the torsion spring within the hinge resists that twisting motion, ensuring the door closes smoothly. Torsion springs are commonly found in various applications, including:
Springs, on the other hand, are designed to resist either compression or extension forces. They are often made of coiled wire, but their function focuses on storing energy by compressing or stretching. A simple example is a spring-loaded toy: when you compress the spring, you store energy, and when you release it, the spring releases the stored energy, propelling the toy forward.
Springs come in various types, each tailored to a specific function. Here's a glimpse of common spring types:
Understanding the fundamental differences between torsion and springs is crucial for choosing the right mechanism for your application. Here's a breakdown:
The choice between torsion and springs depends on the specific needs of an application. Here are a few examples of how they are used in different situations:
Torsion and springs are essential components in a wide range of applications, from everyday objects to complex engineering systems. Understanding the differences between these two mechanisms is crucial for selecting the most appropriate solution for your specific needs. Torsion, with its focus on rotational forces, excels in applications requiring controlled twisting and torque storage. Springs, with their linear movement capabilities, are essential for storing energy, cushioning impacts, and providing retracting forces. The next time you encounter a twisting or spring-loaded object, take a moment to appreciate the intricate mechanics and the underlying principles that make these components so versatile and indispensable in our world.
Whether it's the smooth operation of a door hinge or the bounce of a spring-loaded toy, torsion and springs are ubiquitous in our world. Recognizing their unique properties and applications allows for a deeper appreciation of the mechanics that shape our everyday experiences.
Browse some of the custom wire forms and springs that we manufacture. Don’t see what you need? We specialize in made-to-order products that meet your application requirements.
Visit Our GalleryNeed a custom wire form or coil spring? We make it work. Fill out the contact form and a representative will respond within 1 business day. If you have a PDF or CAD file, you can submit to request a quote.