Get unique, complex parts easily. No matter your requirements, Chaoyi Spring creates hard-to-produce coil springs and wire forms.
Let us help you create the custom wire form you need, from S-hooks and J-hooks to utility hooks and more.
We work closely with customers across a wide range of industries, helping them design and manufacture made-to-order parts.
Why choose Chaoyi Spring? We prioritize customer-focused collaboration, modern equipment and the latest technology to make your parts per print.
Find the information and guidance you need, from measuring a spring to learning about materials, placing an order and much more.
In the world of mechanics, springs are ubiquitous, quietly working behind the scenes to provide force, support, and motion. But when you delve deeper into the world of springs, you


In the world of mechanics, springs are ubiquitous, quietly working behind the scenes to provide force, support, and motion. But when you delve deeper into the world of springs, you find a fascinating variety of types, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Two prominent types are torsion springs and tension springs, each playing a crucial role in different mechanical systems. This article will delve into the fundamental differences between these two types of springs, exploring their construction, operation, and applications, to help you better understand their unique roles in the world of mechanics.
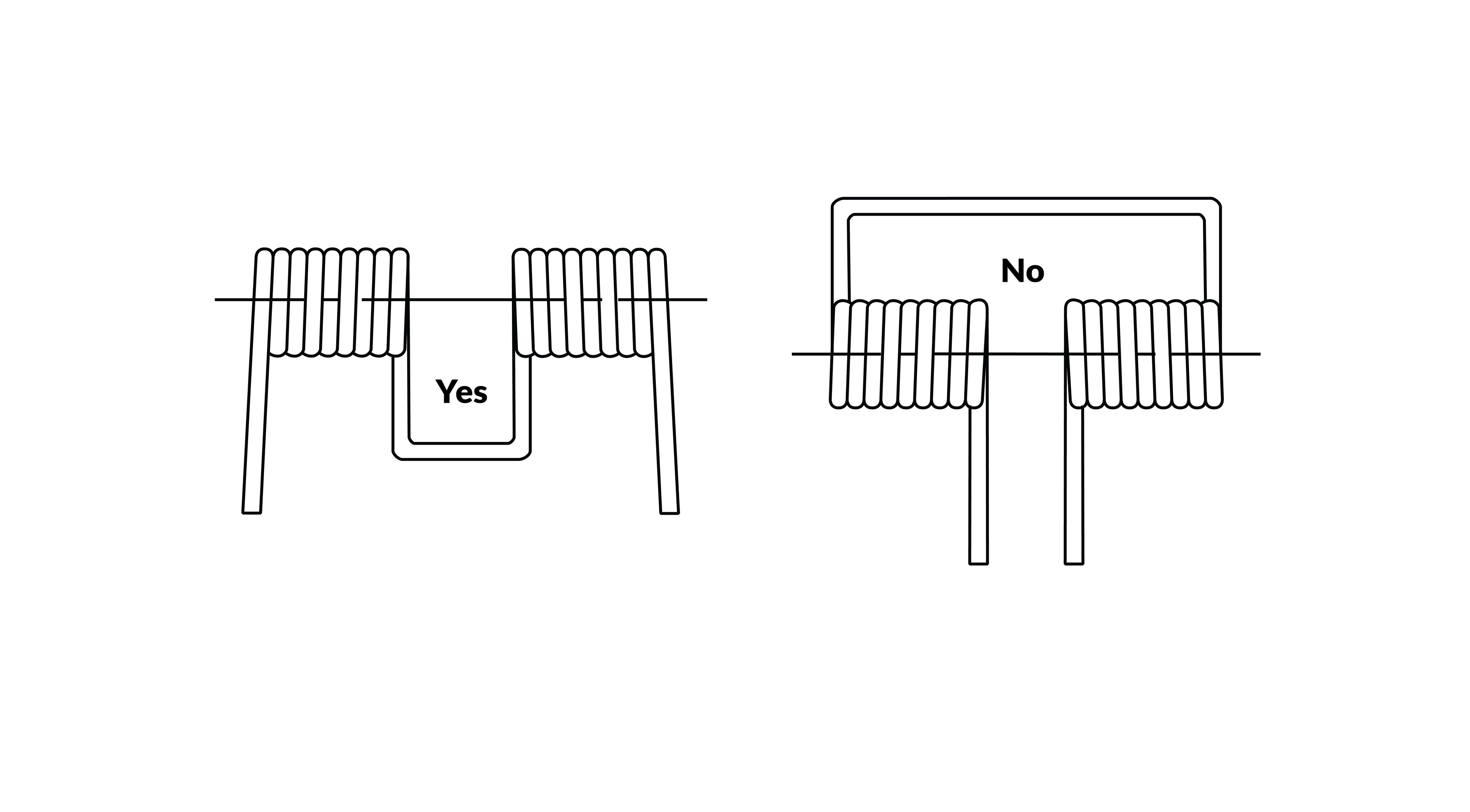
Torsion springs, as the name suggests, are designed to store and release energy through twisting motion. Imagine a classic spring-loaded clothespin, its central bar twisting as it clamps onto your clothes. This is the quintessential example of a torsion spring in action. The spring itself is typically made of coiled wire, but its unique feature lies in the way it's mounted. Instead of being fixed at both ends like a tension spring, a torsion spring is fixed at one end and allowed to rotate freely at the other.
When a torque is applied to the free end of a torsion spring, it twists, storing energy in the process. This stored energy is then released when the torque is removed, causing the spring to unwind back to its original position. The amount of force exerted by a torsion spring is directly proportional to the angle it's twisted. You can think of it like a coiled rubber band, where the more you twist it, the more forcefully it wants to return to its original shape.
Tension springs, on the other hand, are designed for linear motion, working by stretching and contracting under tensile force. Picture a classic bungee cord, extending and retracting as someone jumps off a bridge. That's a perfect example of a tension spring in action. Tension springs typically have loops or hooks at their ends for attachment to objects. When a load is applied to these attachment points, the spring stretches, storing energy in its elongated state.
As the load is released, the spring contracts, attempting to return to its original length. The force exerted by a tension spring is directly proportional to how much it's stretched. Think of it like a rubber band stretched between two points – the more you stretch it, the more it wants to snap back to its original position.
While both torsion and tension springs store and release energy, their fundamental differences are crucial for understanding their applications. Here's a breakdown of the key distinctions:
Torsion springs store energy through twisting motion, while tension springs work through stretching and contracting. This difference in motion dictates their suitability for different applications.
Torsion springs are typically fixed at one end and allowed to rotate freely at the other, while tension springs are often fixed at both ends. The way a spring is mounted determines its overall behavior and the type of load it can handle.
The force exerted by a torsion spring is proportional to the angle it's twisted, while the force exerted by a tension spring is proportional to its elongation. Understanding these relationships is essential for designing and using springs in various applications.
The specific applications of torsion and tension springs are diverse, reflecting the unique properties of each type. Here's a look at some common uses:
The selection of a torsion or tension spring depends entirely on the specific application and the forces involved. Consider these factors when choosing the right spring:
Torsion and tension springs are fundamental components in a wide range of mechanical systems, each playing a distinct role in storing and releasing energy. By understanding their unique characteristics and applications, you can appreciate the power and versatility of these ubiquitous mechanical elements. Whether it's the smooth action of a door closer or the controlled bounce of a trampoline, springs continue to be indispensable in countless aspects of our daily lives.
In the grand tapestry of engineering, springs are the invisible threads that bind together countless mechanisms, ensuring smooth operation and controlled movement. Understanding the distinct qualities of torsion and tension springs is a crucial step in appreciating the remarkable ingenuity and practicality that underpin our modern world. From the smallest watch to the largest industrial machinery, these seemingly simple mechanical elements continue to play a vital role, driving innovation and shaping our technological landscape.
Browse some of the custom wire forms and springs that we manufacture. Don’t see what you need? We specialize in made-to-order products that meet your application requirements.
Visit Our GalleryNeed a custom wire form or coil spring? We make it work. Fill out the contact form and a representative will respond within 1 business day. If you have a PDF or CAD file, you can submit to request a quote.